Littelfuse (LFUS)

Key Statistics
EV/EBIT = 31.98x
ROE = 4.74%
Debt/Equity = 35%
FCF Yield = 4.8%
Dividend Yield = 1.15%
Market Cap = $6.44 billion
The Company
Littelfuse (LFUS) is a global manufacturer of electrical protection and power-control components that are used in a wide range of industries. Its products might be small and easy to overlook, but they are essential for keeping devices, vehicles, and industrial systems safe and working correctly.
Littelfuse has executed a highly successful long-term acquisition strategy, using many targeted deals to expand into complementary technologies, strengthen its leadership in mission-critical electrical components, and position itself at the center of trends such as electrification, automation, and energy efficiency.
As technology becomes more electrified, automated, and connected, the demand for Littelfuse’s parts has steadily increased. The company’s offerings include fuses, circuit protectors, sensors, switches, relays, and semiconductors.
Through its Zilog subsidiary, Littelfuse also develops microprocessors and microcontrollers that bring intelligence and control to these systems. Most of its products are sold directly to manufacturers and distributors around the world, making Littelfuse an important behind-the-scenes player in many industries.
The company’s story began in 1927, when engineer Edward V. Sundt created a fast-acting fuse to protect sensitive diagnostic equipment. At the time, electrical failures were a frequent problem at companies like General Electric and Stewart-Warner, where Sundt worked.
His invention addressed a clear need, and the business he started eventually became Littelfuse Laboratories, later incorporating as Littelfuse, Inc. in 1938. By 1962, Littelfuse had grown large enough to become a publicly traded company. A year later, it relocated its headquarters to Des Plaines, Illinois. In 1968, the company was purchased by Tracor, beginning a period of corporate restructuring and expansion.
The 1970s and 1980s marked major milestones in Littelfuse’s growth. In 1976, it introduced the blade-type automotive fuse, a compact and reliable component that quickly became the standard in cars. Around the same time, Littelfuse began expanding production facilities, opening factories in Mexico and Europe to support global customers. The company’s ownership changed hands again in 1987 when Tracor was acquired by Westmark, but Tracor’s financial troubles led Littelfuse to regain independence in 1991. This shift allowed the company to focus on its own development and begin an ambitious period of acquisitions and product expansion.
Throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, Littelfuse used acquisitions to expand its expertise and product offerings. Key deals included Harris Suppression in 1999, Semitron in 2002, Teccor in 2003, and Heinrich Industrie in 2004, which helped the company diversify into new technologies and global markets. A major leap came in 2017–2018 with the purchase of IXYS, a semiconductor manufacturer, which also brought Zilog, a respected microcontroller and embedded processor company, into the fold. Zilog’s chips add intelligence and programmability to electrical systems, strengthening Littelfuse’s focus on power management and protection.
Since then, Littelfuse has pursued an aggressive acquisition strategy to broaden its capabilities. The company added Hartland Controls in 2021 for HVAC components, Carling Technologies in 2021 for power distribution, Embed in 2022 for embedded software, C&K Switches in 2022 for high-performance interconnect solutions, and Western Automation in 2023 for advanced shock protection devices. These acquisitions strengthened Littelfuse’s presence in high-growth sectors like electrification, renewable energy, and industrial safety.
The most recent milestone was the December 2024 purchase of the Dortmund Fab from Elmos Semiconductor, a 200mm wafer manufacturing facility in Germany. This acquisition significantly increases Littelfuse’s production capacity for power semiconductors, which are essential for regulating and controlling electricity in demanding applications such as electric vehicles, renewable energy storage systems, automation, and industrial equipment.
By owning Dortmund, Littelfuse gains more control over its supply chain and manufacturing capacity, an increasingly important factor as demand for energy-efficient power electronics grows.
Around the same time, Littelfuse opened a modern factory in Piedras Negras, Mexico. This plant, built with sustainable practices in mind, doubles the company’s production capacity in the region and allows for faster delivery of components to North and South American customers. Littelfuse also introduced its Nano² 415 SMD fuse, a compact but powerful fuse capable of handling 1,500 amps at 277 volts.
This product represents an important advancement for industries that need high-performance protection in small spaces, like electric vehicles and renewable energy equipment.
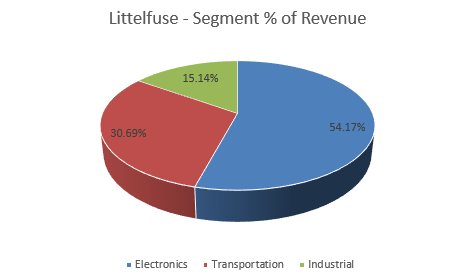
Littelfuse organizes its business into three main segments: Electronics, Transportation, and Industrial.